Click Help→Samples→  to open the Amplifier sample project.
to open the Amplifier sample project.
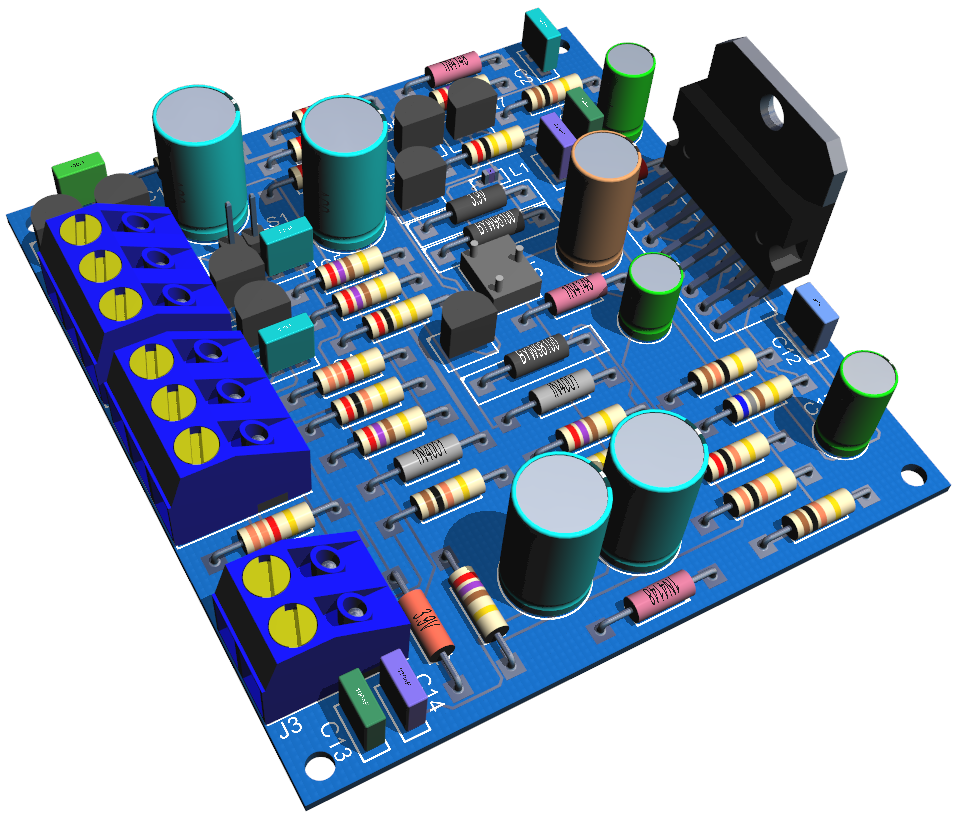
The Amplifier Sample Project
The amplifier project shows a sample design of an amplifier using all TPH components.
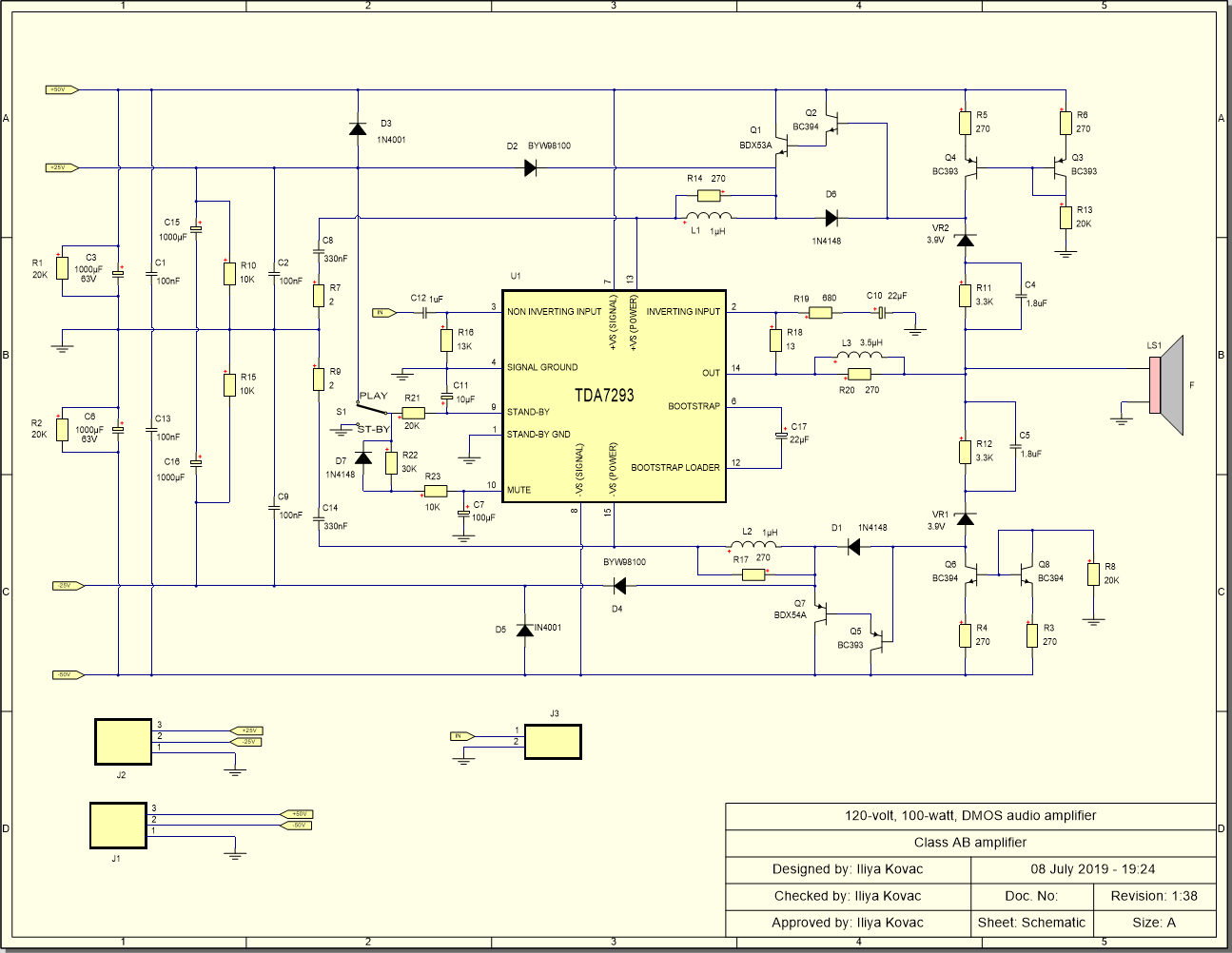
The Main Schematic for the Amplifier
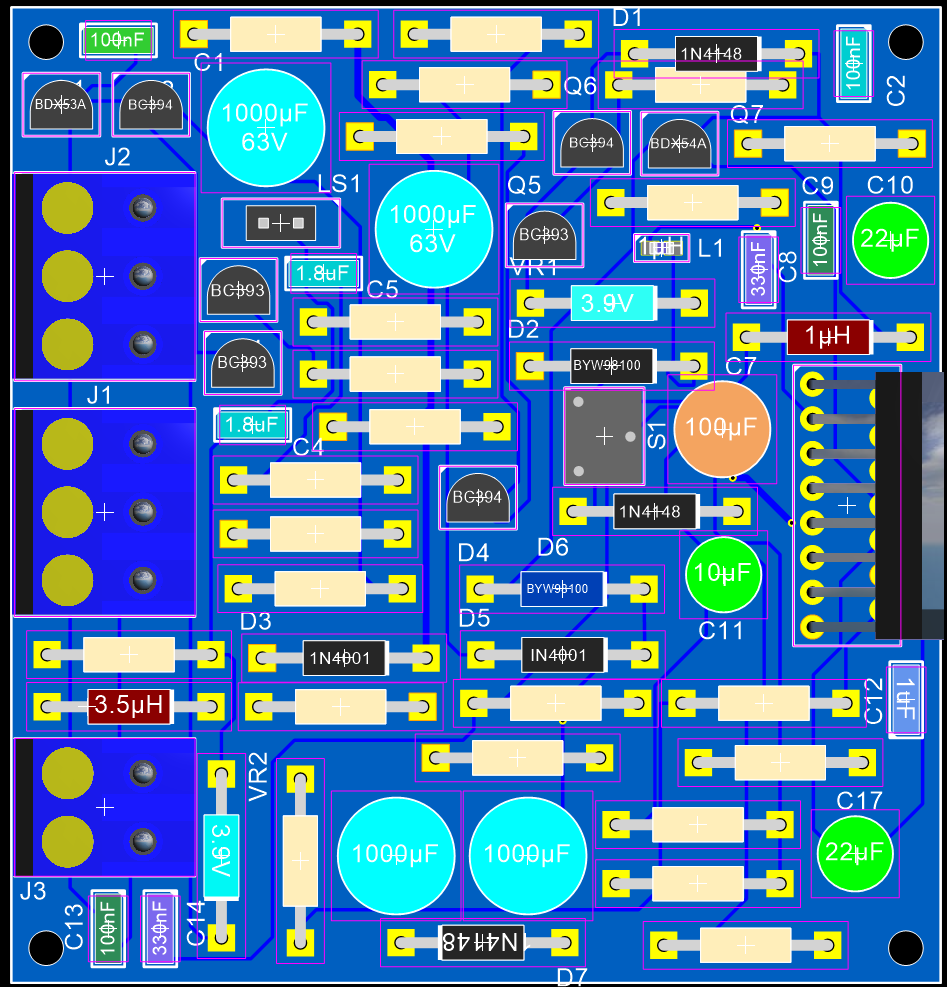
The PCB view in 2-D with all layers on and the PCB set to draw as solid.
Electronic Amplifiers
Electronic amplifiers, or simply amplifiers, are devices that increase the power of a signal. They do this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal's shape but with a larger amplitude. In other words, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal.
Amplifiers are used in a wide range of electronic devices. Here are some types of electronic amplifiers:
•Audio Amplifiers: These are used in home theater systems, radios, and musical instruments (like electric guitars) to increase sound levels.
•Radio Frequency (RF) Amplifiers: These amplify signals in the radio frequency range, which are used in wireless communication devices like mobile phones, and in broadcast transmitters.
•Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps): These are used in a wide range of applications, including signal conditioning, filtering, or for performing mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, integration, and differentiation.
•Instrumentation Amplifiers: These are used in the amplification of signals from instruments like strain gauges and thermocouples. They're designed to provide high input impedance and high gain while rejecting unwanted noise.
•Microwave Amplifiers: These are used to amplify signals in the microwave frequency range, typically used in radar systems and satellite communications.
The performance of an amplifier is characterized by several parameters, including gain (the ratio of the output signal power to the input signal power), bandwidth (the range of frequencies over which the amplifier provides satisfactory performance), efficiency, linearity, noise figure, and others.
There are also many different types of amplifier circuits, each designed to maximize certain performance parameters depending on the intended application. The most common types are Class A, B, AB, and D, each providing a unique balance of power efficiency, linearity, and distortion characteristics.