
A PCB Transformer
Potentiometers, often referred to as pots, are a type of resistor with a third terminal that forms an adjustable voltage divider. They are used to measure electromotive force or to control electrical devices such as volume controls on audio equipment. Potentiometers can be used as a rheostat (two-terminal variable resistor), or as a true potentiometer (three-terminal device).
When it comes to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), PCB potentiometers are simply potentiometers designed to be mounted on these boards. They come in many different forms, sizes, and complexities, but they all function by changing the resistance value in a circuit.
The two most common types are:
Rotary Potentiometers
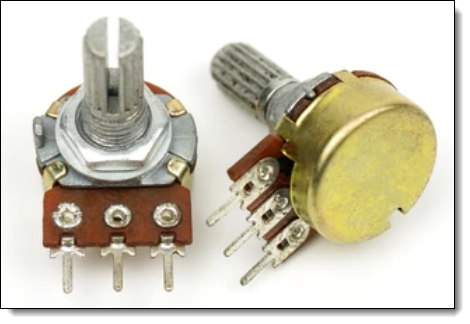
Two PCB Transformers
These have a rotating shaft that you turn to change resistance. They are often used in applications such as audio volume control or light dimmer switches.
Slide or Linear Potentiometers
These have a slider which moves along a linear path to change resistance. They are often used in mixing boards and light controls.
Adjustments to the potentiometer modify the flowing current, enabling fine-tuning of the connected electrical devices. For instance, a potentiometer might be used on a PCB inside a radio to adjust the volume, or in a light fixture to adjust the brightness of the light. The specific design and use of a PCB potentiometer can vary widely depending on its intended application.