You can add 4 types of transistor to your design.
A BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) is a type of transistor that uses both electron and hole charge carriers for operation. It has three terminals: base, collector, and emitter. BJTs come in two types: NPN and PNP. They are used to amplify or switch electronic signals by controlling the flow of current between the collector and emitter, with a small current applied to the base. In an NPN transistor, current flows from the collector to the emitter, while in a PNP, it flows in the opposite direction. BJTs are widely used in analog circuits.
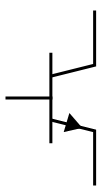 NPN Transistor |
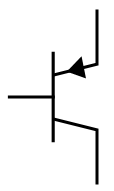 PNP Transistor |
A JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) is a type of transistor that controls current flow using an electric field. It has three terminals: gate, drain, and source. Unlike BJTs, JFETs are voltage-controlled devices, meaning a voltage applied to the gate regulates the current between the drain and source. JFETs come in N-channel and P-channel types, where current flows through an N-type or P-type semiconductor channel, respectively. They are known for having high input impedance, making them useful in applications requiring minimal power consumption or signal distortion, such as amplifiers and switches.
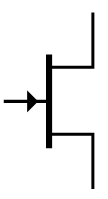 N-Channel JFET |
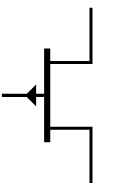 P-Channel JFET |
A MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is a type of transistor that controls current using an electric field. It has three main terminals: gate, drain, and source. MOSFETs are voltage-controlled devices, meaning the voltage applied to the gate controls the current flow between the drain and source. They come in two types: N-channel and P-channel, with N-channel being more common. MOSFETs are widely used for switching and amplifying signals, especially in digital circuits and power electronics, due to their fast switching speed, low power consumption, and high efficiency.
A MESFET (Metal-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is a type of field-effect transistor that uses a metal-semiconductor junction (Schottky barrier) instead of a traditional p-n junction. It has three terminals: gate, drain, and source, similar to a JFET or MOSFET. MESFETs are commonly used in high-frequency applications, such as microwave and RF circuits, because of their ability to operate at higher speeds. They are typically made from compound semiconductors like gallium arsenide (GaAs), which allows them to perform better in high-frequency and high-power conditions compared to silicon-based transistors.