To save the current view to an image file click the Tools→Export→ button.
button.
Maximum Size
Enter the maximum pixel/resolution size. The image saved is the same aspect ratio of the current viewport. So, to change the viewport aspect ratio, re-size the viewport.
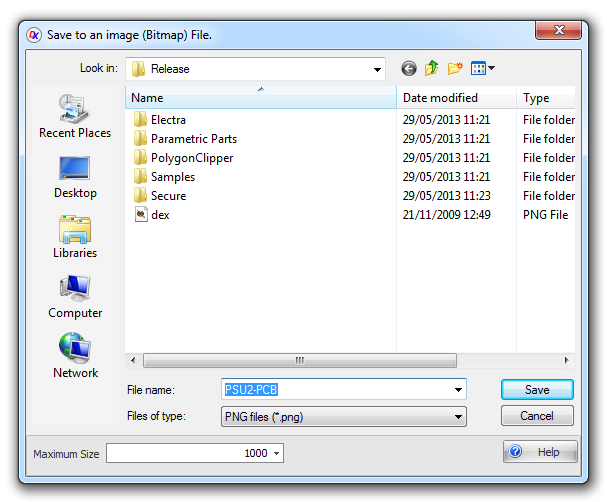
Save to Image Dialog
Maximum Size - Enter the maximum dimension of the image in pixels. The other dimension will be set by the aspect ratio of the current viewport.
 Click to show this help topic.
Click to show this help topic.You can save to the following formats:
BMP
The BMP file format, also known as bitmap image file or device independent bitmap (DIB) file format or simply a bitmap, is a raster graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device (such as a graphics adapter), especially on Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems.
EMF
In 1993, the 32-bit version of Win32/GDI introduced the Enhanced Metafile (EMF), a newer version with additional commands. EMF is also used as a graphics language for printer drivers. Microsoft recommends that "Windows-format" (WMF) functions only "rarely" be used and "enhanced-format" (EMF) functions be used instead.
EXIF
Exchangeable image file format (Exif) is a standard that specifies the formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smart phones), scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras
GIF
The Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) is a bitmap image format that was introduced by CompuServe in 1987 and has since come into widespread usage on the World Wide Web due to its wide support and portability. The format supports up to 8 bits per pixel thus allowing a single image to reference a palette of up to 256 distinct colors. The colors are chosen from the 24-bit RGB color space. It also supports animations and allows a separate palette of 256 colors for each frame. The color limitation makes the GIF format unsuitable for reproducing color photographs and other images with continuous color, but it is well-suited for simpler images such as graphics or logos with solid areas of color.
GIF images are compressed using the Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) lossless data compression technique to reduce the file size without degrading the visual quality. This compression technique was patented in 1985. Controversy over the licensing agreement between the patent holder, Unisys, and CompuServe in 1994 spurred the development of the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) standard. All the relevant patents have now expired.
PNG
Portable Network Graphics (PNG) is a raster graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was created as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), and is the most used lossless image compression format on the World Wide Web. The motivation for creating the PNG format was in early 1995, after it became known that the Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) data compression algorithm used in the Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) format was patented by Unisys. There were also other problems with the GIF format that made a replacement desirable, notably its limit of 256 colors at a time when computers able to display far more than 256 colors were growing common. Although GIF allows for animation, it was decided that PNG should be a single-image format.
JPG
JPEG is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital photography (image). The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10: 1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.
TIFF
TIFF (originally standing for Tagged Image File Format) is a file format for storing images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry,]and both amateur and professional photographers in general. As of 2009, it is under the control of Adobe Systems. Originally created by the company Aldus for use with "desktop publishing", the TIFF format is widely supported by image-manipulation applications, by publishing and page layout applications, by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition and other applications.[3] Adobe Systems, which acquired Aldus, now holds the copyright to the TIFF specification. TIFF has not had a major update since 1992.
WMF
Windows Metafile (WMF) is an image file format originally designed for Microsoft Windows in the 1990s. Windows Metafiles are intended to be portable between applications and may contain both vector graphics and bitmap components. It acts in a similar manner to SVG files.