Back annotation in the context of printed circuit board (PCB) design is the process of transferring changes from the PCB layout back to the schematic.
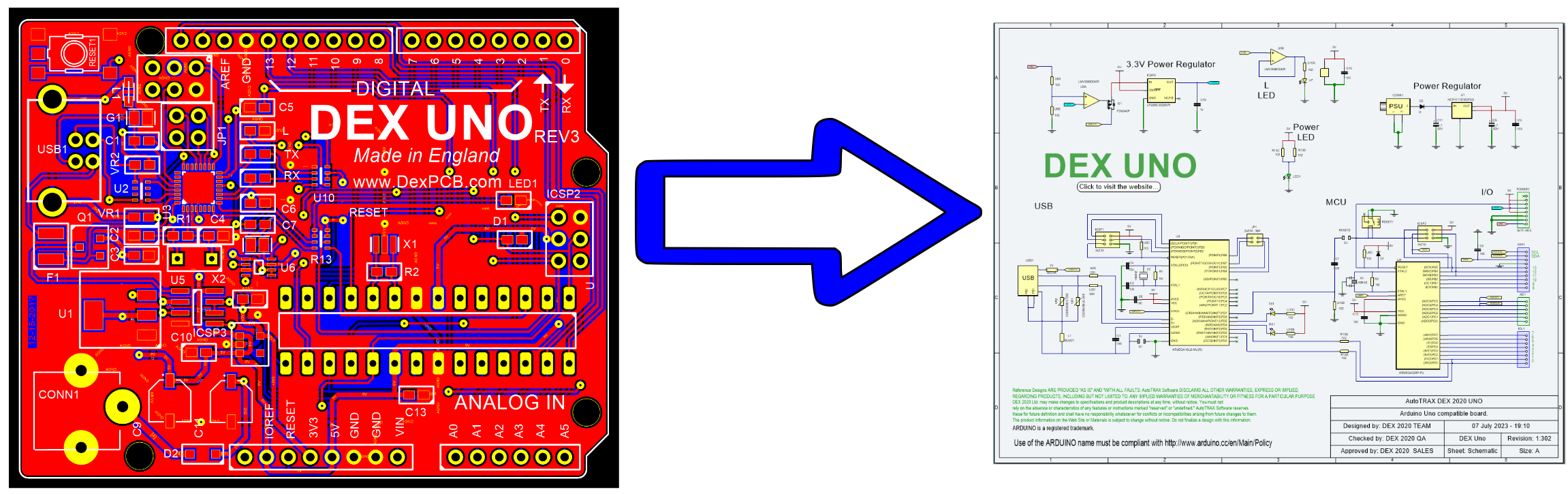
PCB Back Annotation
When designing a PCB, you typically start by creating a schematic, which is a diagram that represents the electrical connections between different components. This schematic is then used to create a physical layout for the PCB.
Sometimes, changes are made during the PCB layout process. These might include changing component values, or reordering the components for space optimization, improved signal integrity, or other considerations. These changes can significantly affect the electrical properties and behavior of the circuit.
Back annotation is the process of taking these changes and updating the original schematic to reflect them. This is important for a few reasons:
Consistency
It's important to have a single, consistent representation of the design. If the schematic and layout don't match, it can cause confusion and mistakes.
Verification and Validation: Many of the analyzes and checks that are done during the design process (like circuit simulation, design rule checks, etc.) are based on the schematic. If the schematic doesn't reflect the actual design, these analyzes may not be accurate.
Documentation
The schematic is often used as a basis for creating other documentation, like the Bill of Materials (BOM), assembly drawings, and so on. If it's not up to date, these documents will be incorrect.
It's worth noting that the specifics of how back annotation is done can depend on the particular Electronic Design Automation (EDA) software you're using. In some cases, the software may be able to automatically apply changes from the layout to the schematic. In other cases, you may need to manually update the schematic based on a report of changes from the layout tool.