To specify the design of a PCB, you need to provide clear and detailed information about the requirements, constraints, and specifications for the design. Here are some key aspects to consider when specifying a PCB design:
Purpose and Functionality
Clearly define the purpose and functionality of the PCB. Describe what the circuit is intended to do, its intended application, and any specific features or requirements it should fulfill.

Deciding on PCB Design and Functionality
Board Size and Shape
Specify the physical dimensions and shape of the PCB. Consider factors such as the available space in the enclosure or system where the PCB will be installed, as well as any size limitations or constraints.

PCB Board Size
Layer Configuration
Determine the number of layers required for the PCB. Consider the complexity of the circuit, the density of components, and the need for signal integrity. Specify the stack-up configuration, such as the placement of signal layers, ground planes, power planes, and any other specific requirements.
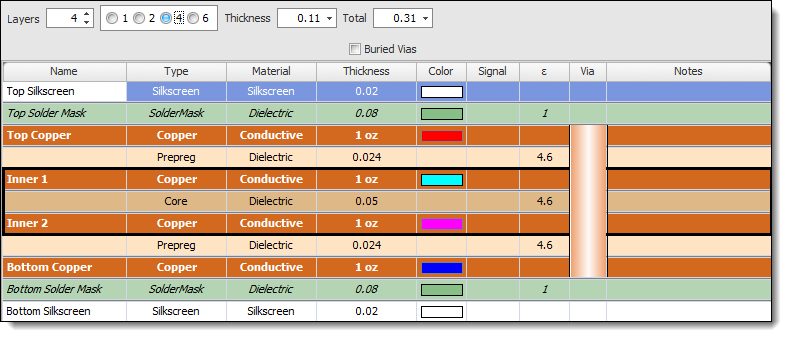
PCB Layer Configuration
Component Placement
Specify any specific requirements for component placement. If there are critical components that require specific locations or orientations, mention them. Consider factors such as thermal considerations, signal routing, and accessibility for assembly and testing.
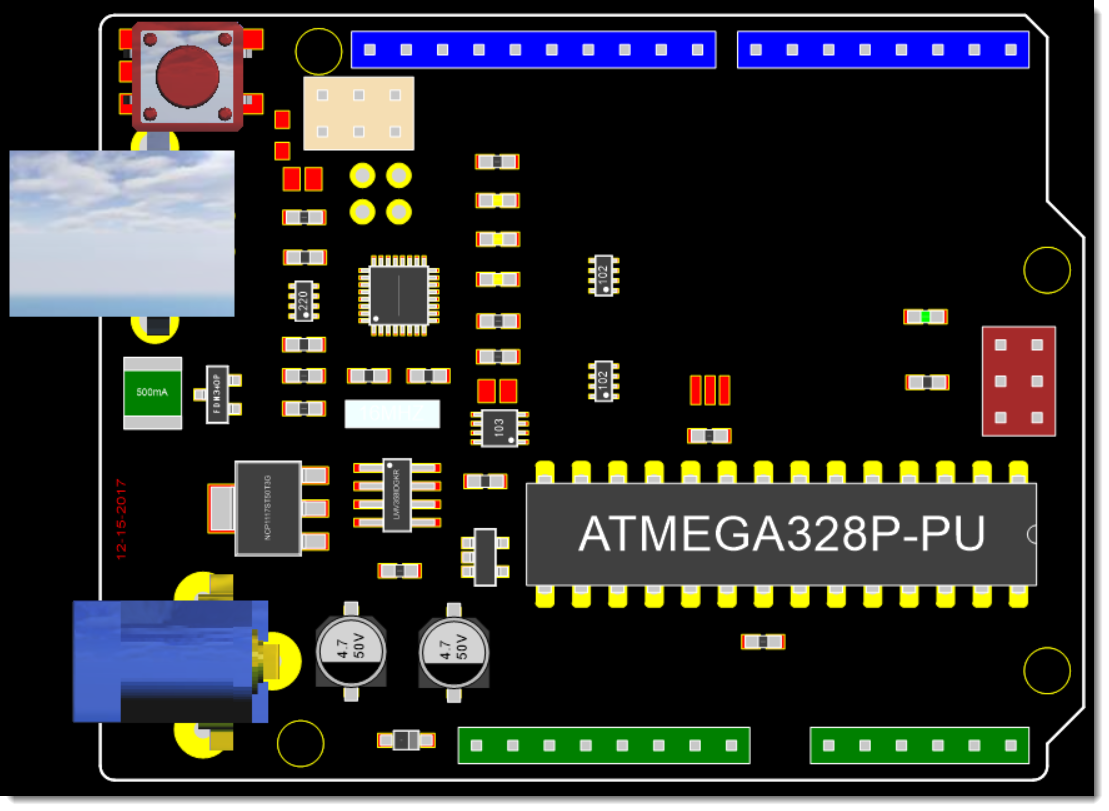
PCB Component Placement
Define the electrical specifications for the PCB. Specify the voltage and current requirements, impedance matching requirements, signal integrity considerations, and any specific power supply or signal conditioning requirements.
Design Constraints
Identify any design constraints or limitations. For example, specify any specific manufacturing constraints, such as minimum trace width and spacing, via size, and drill requirements. Consider any specific environmental or operational constraints that may impact the design.

Deciding on PCB Dersig Constraints
Connectivity and Interfaces
Specify the connectors, interfaces, or communication protocols required for the PCB. Identify any specific pin assignments, connector types, or signal levels that need to be incorporated into the design.

PCB Connectivity
Manufacturing Requirements
Specify any specific manufacturing requirements, such as solder mask color, silkscreen legends, surface finish, and any special fabrication techniques or processes required.

PCB Manufacturing Requirements
Testing and Quality Assurance
Define any specific testing requirements or quality assurance procedures that need to be followed during the manufacturing and testing phases. Specify any testing points or test pads required for debugging or functional testing.
PCB Testing and Quality Assurance
Documentation
Clearly specify the level of documentation required for the PCB design. This may include schematic diagrams, Bill of Materials (BOM), assembly drawings, PCB layout files, and any other relevant documentation.
When specifying the design of a PCB, it's crucial to be as detailed and specific as possible. This helps ensure that the PCB designer or manufacturer can accurately understand and meet your requirements. If you are unsure about any specific aspects of the design, consider consulting with an experienced PCB designer or engineer to assist you in the specification process.

PCB Documentation