To create/export to a SVG file click the Tools→Export→ button.
button.
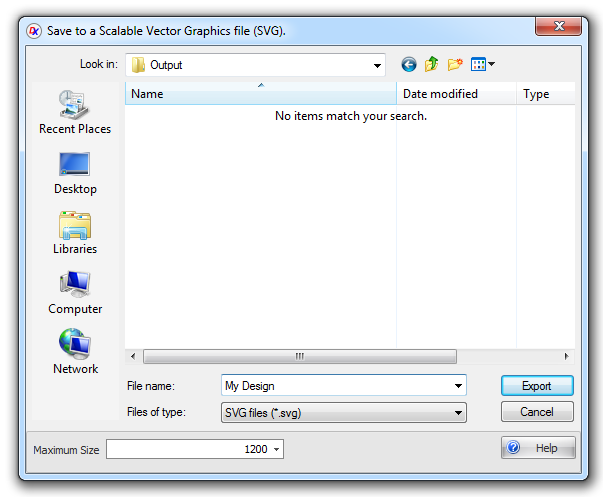
SVG export dialog
Maximum Size - Enter the maximum dimension of the image in pixels. The other dimension will be set by the aspect ratio of the contents.
 Click to show this help topic.
Click to show this help topic.All major modern web browsers—including Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer 9 and 10, Google Chrome, Opera, and Safari—have at least some degree of support for SVG and can render the markup directly.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is a widely used XML-based vector image format that is primarily used for displaying two-dimensional graphics and animations on the web. Unlike raster image formats like JPEG or PNG, SVG images are resolution-independent and can be scaled without losing quality. SVG files describe images using mathematical shapes and text rather than a grid of pixels, making them ideal for logos, icons, illustrations, and other graphics that need to maintain their clarity at various sizes.
Key features of SVG files include:
•Vector Graphics: SVG images are defined using geometric shapes such as lines, curves, and polygons, allowing them to be scaled up or down without loss of quality.
•XML-Based: SVG files are written in XML format, which means they are human-readable and can be easily edited using a text editor or specialized software.
•Scalability: SVG images can be re-sized without loss of detail. This makes them suitable for responsive web design, where graphics need to adapt to different screen sizes.
•Support for Styling: SVG supports a range of styling options including colors, gradients, transparency, and custom CSS properties.
•Text Support: SVG files can include text elements, allowing them to display text along with graphical elements.
•Interactive and Animatable: SVG images can include interactivity and animations using CSS and JavaScript.
•Web Compatibility: SVG is supported by all modern web browsers, making it a popular choice for web-based graphics.
SVG files are used for various purposes:
•Web Graphics: SVG is commonly used for creating graphics on websites, such as logos, icons, buttons, and illustrations.
•Data Visualization: SVG is used to create dynamic and interactive charts, graphs, and data visualizations.
•Icons: SVG icons are widely used due to their ability to be scaled while maintaining crisp edges.
•Animations: SVG animations are used for creating simple animations and transitions on web pages.
•Print Design: SVG files can be used in print design, though they might require conversion to other formats like PDF for high-quality printing.
•Accessible Graphics: SVG images can be used to create graphics that are accessible to users with disabilities.
When using SVG files, keep in mind that complex images with numerous intricate details might increase file size, affecting load times on web pages. Additionally, while SVG files are great for most types of graphics, they might not be suitable for images that require high levels of photo-realism or complex textures.